You're comparing two plastic seals. The spec sheet for one boasts about the "high tensile strength" of its HDPE material. The other highlights the "superior heat resistance" of its PP construction. Which is actually more secure?
This choice feels like a trade-off, forcing you to pick one benefit over the other. This uncertainty can lead to selecting a seal that's fundamentally mismatched to the real threats your cargo faces, leaving you with a false sense of security.
The choice between HDPE and PP isn't about strength versus heat resistance; it's about choosing the right "Evidence Presentation Mechanism." HDPE's tensile strength provides clear evidence against physical, brute-force attacks, while PP's thermal and chemical stability provides durable evidence in harsh environmental conditions.
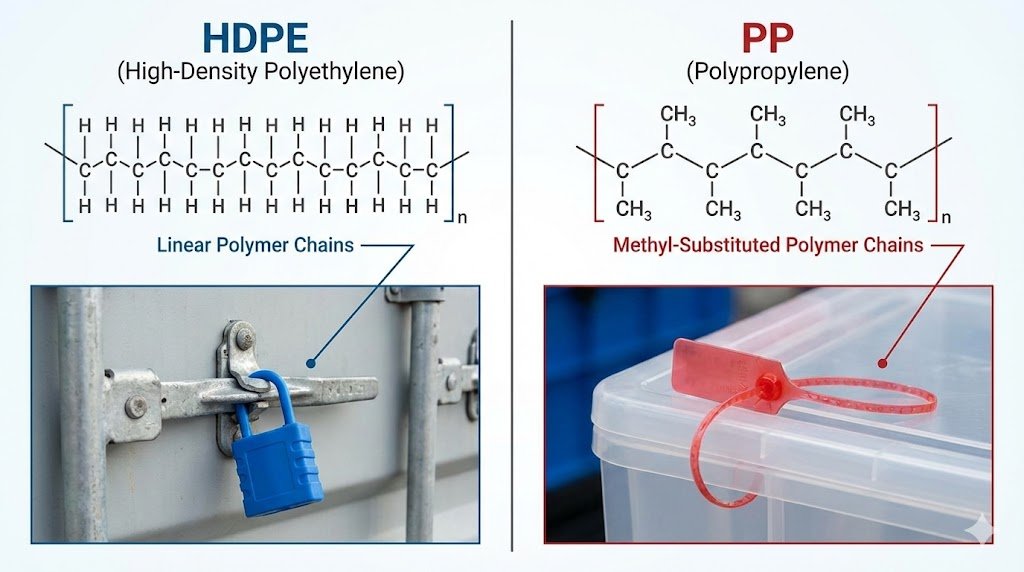
When I first started in quality control, I saw this as a simple physics problem. I would test seals for their breaking points and heat tolerance. But after years of analyzing failed and tampered seals from the field, I realized a much deeper truth. The debate about HDPE's "strength" and PP's "heat resistance" is not a battle between material properties. Instead, these are two fundamentally different "Evidence Presentation Mechanisms." These mechanisms are intentionally designed into security seals to counter specific types of threats. Your job is to match the mechanism to the risk.
A Microscopic Look: How Molecular Structure Dictates Plastic Seal Performance?
Why does one plastic stretch while the other stays rigid? It's not magic; it's chemistry.
The performance differences between HDPE and PP are born from their invisible molecular structures. Understanding this is the foundation for grasping why they behave so differently under attack.
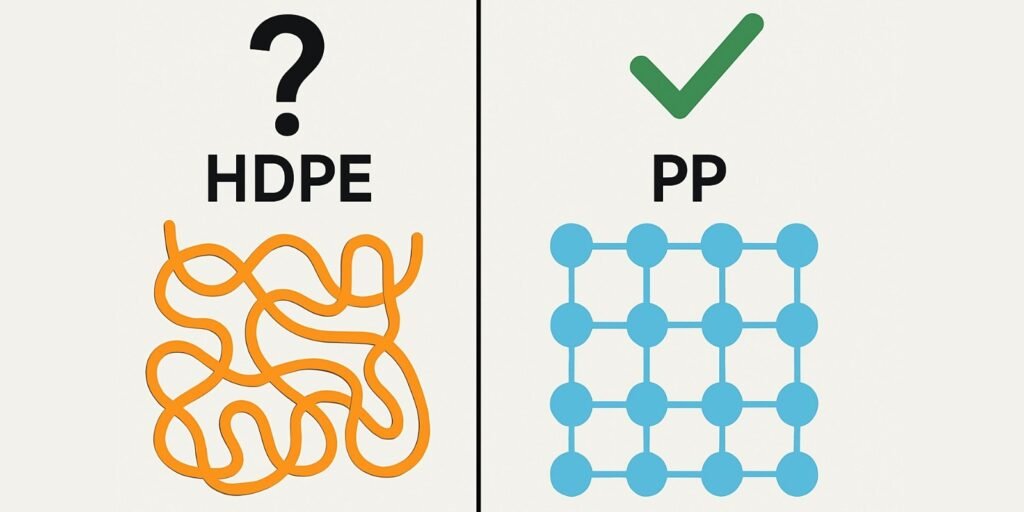
Think of it this way: the long, unbranched polymer chains of HDPE are like a bowl of tangled spaghetti. They are flexible and can slide past each other, but they are incredibly difficult to pull apart, which gives the material its high tensile strength. In contrast, Polypropylene has a more ordered, semi-crystalline structure, almost like neatly stacked bricks. This rigid structure makes it dimensionally stable, especially against heat, but it will snap more cleanly if enough force is applied, rather than stretching. These microscopic differences create the two distinct "evidence mechanisms" that we rely on in the field.
HDPE Seals: Superior Tensile Strength Born for High-Security Applications?
Your shipment is moving across the country by truck, facing rough roads and the constant threat of a brute-force break-in. Which material is your best witness?
This is the exact scenario where you need HDPE's evidence mechanism. Its entire design is geared towards resisting and clearly showing evidence of physical force.
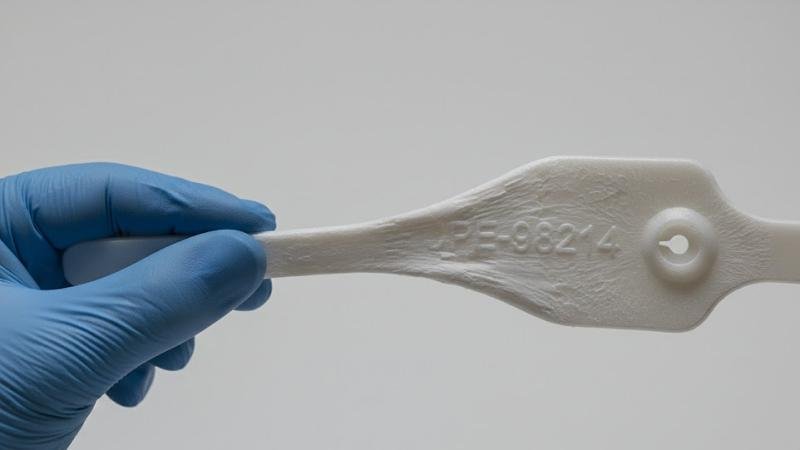
The strength of HDPE is not just about preventing a seal from breaking easily. More importantly, it's about what happens when someone tries. Due to its spaghetti-like molecular structure, when you apply a strong pulling force, the material doesn't snap. It elongates and exhibits dramatic "stress whitening." This visible, irreversible damage is the seal screaming, "Someone tried to pull me apart!" I've seen seals come back from the field that were beaten and pried at, and while the seal held, the bright white stress marks told the whole story. This makes HDPE the premier choice for barrier seals on containers, trailers, and rail cars where tensile strength is the primary line of defense.
PP Seals: Proven Reliability in Extreme Temperatures and Chemical Environments?
Your cargo is a tanker of chemicals, or it's being sealed in Dubai's 45°C heat before traveling through a cold region. How do you ensure the seal itself remains a reliable witness?
Here, the primary threat isn't a pair of bolt cutters; it's the environment itself. This is where you deploy PP's evidence mechanism: its unwavering stability.

PP's rigid, crystalline structure gives it a much higher melting point (around 160°C) and far greater chemical resistance than HDPE. An HDPE seal might soften or deform in extreme heat, creating a "false positive" for tampering or making it easier to manipulate. A PP seal, however, will maintain its form and integrity. Its evidence mechanism is its refusal to change. It will only show signs of tampering (like melting or discoloration) when exposed to a direct flame or a specific corrosive agent. This makes it an incredibly reliable witness in environments like chemical plants, pharmaceutical facilities, and for any logistics chain passing through punishingly hot climates. It proves its integrity by remaining unchanged.
Practical Considerations: Comparing Seal Flexibility, Marking Capability, and Cost-Effectiveness
Beyond the primary evidence mechanism, how do these materials perform in day-to-day operations?
The choice of material impacts everything from how easily a seal is applied to how clearly you can read its serial number. These practical details are vital for an efficient and secure operation.

A security strategy that is difficult to implement is a strategy that will fail. Over the years, I've helped clients fine-tune their choices based on these secondary, but crucial, factors.
Flexibility and Ease of Use
HDPE is significantly more flexible than PP. This makes it the superior material for adjustable pull-tight seals that need to be cinched down tightly around an object with a small diameter. PP's stiffness is better suited for fixed-length or padlock-style seals.
Marking and Identification
Both materials can be marked, but PP's harder surface often allows for sharper, higher-contrast laser marking. For operations that rely heavily on barcode scanning or OCR for traceability, the crispness of a PP laser mark can be a meaningful advantage, reducing scan errors.
Cost-Effectiveness
On a per-unit basis, PP is generally a more economical raw material than HDPE. For high-volume applications where PP's evidence mechanism is a perfect fit (like securing tote boxes in a temperature-controlled warehouse), this lower cost can lead to substantial savings without any compromise in effective security.
Data for Your Decision: A Clear Comparison Chart for Plastic Seal Materials
How can you quickly summarize all this information to make the right choice for your next shipment?
This decision-making process can be simplified. Here is a clear, at-a-glance comparison of the two materials based on the factors we've discussed.
Use this chart as your final checklist. Match your primary threat and operational needs to the material that provides the best solution.
| Feature | High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) | Polypropylene (PP) |
|---|---|---|
| Molecular Structure | Long, unbranched polymer chains | Ordered, semi-crystalline |
| Primary Strength | High Tensile & Impact Strength | High Rigidity & Hardness |
| Heat Resistance | Good (up to ~120°C) | Excellent (up to ~160°C) |
| Cold Resistance | Excellent (maintains flexibility) | Fair (can become brittle) |
| Chemical Resistance | Good | Excellent |
| Evidence Mechanism | Physical Deformation (Stretching, stress whitening) | Environmental Stability (Resists heat/chemicals) |
| Best Application | Barrier seals, cross-border transport, high-value cargo | Chemical/oil tankers, hot climates, color-coding |
Conclusion
The best plastic seal material is the one with the right evidence mechanism for your specific risks. Choose HDPE to combat physical force and PP to withstand environmental extremes. This strategic choice is the foundation of true security.
Match the Mechanism to the Mission with ProtegoSeal
Stop choosing seals based on a single spec. At ProtegoSeal, we analyze your entire supply chain to recommend the seal with the precise evidence presentation mechanism your security requires. Contact us for a strategic consultation.