You think using a security seal is simple—just click it shut, right? I've seen this assumption lead to rejected shipments, failed compliance audits, and significant financial losses. A seal is only as strong as the protocol built around its entire lifecycle.
A complete security seal protocol covers four key stages: secure storage before use, correct application and documentation, safe removal and inspection, and finally, responsible disposal or recycling. Each step is critical for maintaining an unbroken chain of custody and ensuring the seal is verifiable, tamper-evident proof.

In my early projects, I focused only on the physical strength of the seal. A painful experience with a client shipping high-value electronics taught me a hard lesson. Their seals were intact, but their documentation was a mess. When customs flagged a container, they couldn't produce a coherent seal log. The resulting inspection and delay cost them over $20,000. That's when I realized the procedure is what gives the seal its power. Let's walk through that professional procedure.
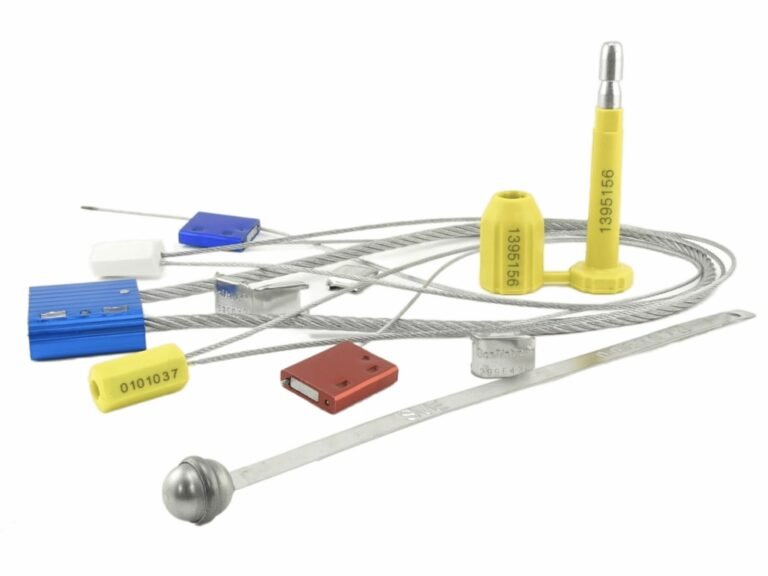
What Are the Core Types of Security Seals?
Choosing the wrong type of seal for the job is a common first mistake. You wouldn't use a simple plastic tag to secure an international shipping container. Understanding the main categories is the first step toward building a sound security plan.
The three primary categories are plastic, metal, and electronic seals, each designed for different levels of security and operational needs. Your choice depends on the value of the cargo, the risk of the route, and regulatory requirements like ISO 17712.

Dive Deeper: Matching the Seal to the Mission
In my experience, clients often default to what's cheapest, not what's appropriate. This is a false economy. The cost of one compromised shipment will dwarf years of savings on seals. Here's how I break down the choices for them:
Plastic Seals (Indicative Security)
These are your first line of defense, designed to show evidence of tampering (indicative) rather than provide a strong physical barrier.
- Best For: Courier bags, airline food trolleys, ballot boxes, fire extinguishers. Anything that needs a clear visual "tampered/not tampered" status.
- My Insight: Think of these as a deterrent and a tattle-tale. They won't stop a determined thief, but they will make it impossible for them to hide their actions. A report from the Transported Asset Protection Association (TAPA) often highlights that even low-level indicative seals can deter opportunistic theft.
Metal Seals (Barrier Security)
These seals provide a significant physical barrier to entry. They require specialized tools for removal.
- Best For: Shipping containers, cross-border trucks, rail cars. These are the workhorses of global logistics.
- Types: This category includes heavy-duty Cable Seals and Bolt Seals.
- My Insight: When a client needs to meet ISO 17712 "H" class (High Security) requirements for international shipping, there is no substitute for a compliant bolt seal. Attempting to use a non-compliant seal can lead to cargo being held at port, a disaster for any supply chain.
Electronic Seals (Intelligent Security)
These combine a physical seal with electronic components for real-time tracking and alerts.
- Best For: High-value pharmaceuticals, sensitive government documents, high-tech electronics.
- My Insight: E-seals are a game-changer for supply chain visibility. In one project involving sensitive cargo, an e-seal sent an alert the moment a container door was opened unexpectedly mid-route. This allowed security to intervene in real-time, preventing a potential loss of over $500,000.
How to Store Security Seals for Maximum Integrity?
Leaving new security seals in an open bin on the warehouse floor is your first security failure. What’s to stop someone from taking one, tampering with your shipment, and replacing the original seal with the stolen one?
Secure storage is the first step in the chain of custody. It ensures only authorized personnel access new seals, preventing pre-tampering and fraudulent replacement. This practice is a foundational requirement for security programs like the C-TPAT.

Dive Deeper: Implementing a "First-In, First-Out" (FIFO) Seal Control System
In my projects, I don't just recommend a locked cabinet; I help clients implement a full seal control log. It’s far simpler than it sounds. For one mid-sized logistics company, we built a basic system that drastically improved their security posture:
- Designated Storage: All new seals were moved to a locked cage in the supervisor's office.
- Logbook Implementation: A simple sign-out sheet records: Date, Time, Supervisor's Name, Range of seal numbers issued (e.g., PS123001 - PS123100), and Intended Use.
- FIFO Principle: We organized the boxes by date of arrival. This is crucial for plastic security seals, as materials like polypropylene can become brittle over time with prolonged exposure to a harsh environment.
With this system, we created an audit trail before a seal was even applied. If a seal number ever appeared where it shouldn't, they could instantly trace who took it and when. This proactive step turns a storeroom into your first line of defense.
How to Apply Security Seals Correctly?
Applying a seal incorrectly renders it completely useless. If a pull-tight seal is too loose, it can be slipped off. If a bolt seal isn't fully snapped into place, it offers no real security. This is where physical action and data logging must merge.
Correct application involves physically securing the seal according to its design and immediately documenting its unique identifier in a log. This creates a time-stamped record linking a specific seal to a specific asset, forming the core of your verifiable audit trail.

Dive Deeper: The Application Checklist for Different Seal Types
The "right way" depends entirely on the seal. I’ve seen operators damage seals by using the wrong technique. Here's my application checklist:
| Seal Type | Key Application Step | My Pro Tip |
|---|---|---|
| Plastic Pull-Tight | Thread the tail through the hasp and pull snug. | The Pencil Test: You should not be able to fit more than a pencil's width of slack. On soft bags, be careful not to overtighten. |
| Cable Seals | Pull the cable tight through the locking body. | The Tug Test: Give it a strong, sharp pull to confirm the internal locking mechanism has engaged. The cable must not pull back out. |
| Bolt Seals | Push the pin firmly into the barrel through the latch. | The "Click & Tug": You must hear and feel a loud, distinct "CLICK." Then, try to pull the two pieces apart by hand. If locked correctly, it will not budge. |
Proper application is not just best practice; it's a core component of the ISO 17712 standard. Immediately after application, record the number and, if possible, take a photo. This digital proof is invaluable in disputes.
What is the Correct Way to Remove a Security Seal?
The way a seal is removed is a critical data point. If a seal requires a 24-inch bolt cutter but is found twisted off by hand, that’s an immediate and obvious red flag. An improper removal process is also a serious safety hazard.
Safe removal requires using the correct tool for the seal's security level while wearing appropriate Personal Protective Equipment (PPE). The process itself serves as the final verification step: checking the seal number against the manifest before removal.

Dive Deeper: Matching the Tool to the Threat and Ensuring Safety
I provide all clients with a simple "Tool & Safety" matrix. It prevents both security lapses and costly workplace injuries. According to the U.S. Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA), eye injuries from flying particles are a common and preventable workplace hazard.
Here’s my field-tested safety checklist:
- Verify First: Before reaching for a tool, check the seal number against shipping documents. Inspect for tampering.
- Gear Up: For any metal seal, safety goggles and gloves are mandatory.
- Use the Right Tool:
- Plastic Breakaway: Twist and snap by hand.
- Plastic Pull-Tight: Use safety snips.
- Cable & Bolt Seals: Use heavy-duty bolt cutters (24" or longer). Small cutters are a safety risk.
- Control the Cut: When cutting a seal under tension, turn your face away and ensure no one is standing in front of you.
How to Dispose of and Recycle Used Seals?
Tossing a used seal in the trash creates two problems: it’s a security risk and an environmental waste. A seal with its number intact could potentially be recovered and used to disguise a breach.
Proper disposal involves destroying the seal to prevent reassembly and, where possible, segregating materials for recycling. This final step closes the loop on the seal's life, ensuring it cannot be misused after its purpose is served.

Dive Deeper: A Practical Approach to Seal Waste Management
Most facilities won't have complex recycling programs just for seals, so my approach is to make it simple and effective.
- Security First: The #1 rule is to destroy the seal's unique identifier. For bolt seals, separate the pin and barrel. For plastic and cable seals, cut them into at least two pieces, right through the serial number.
- Recycling Simplified:
- Plastic Seals: Most are made of polypropylene (PP) or nylon. The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) provides guidance on plastics recycling. Check with your local provider if they can handle small items.
- Metal Seals: These are easily recycled. Collect them in a dedicated scrap metal bin.
- Electronic Seals: These are e-waste. They contain batteries and circuits and must be handled according to your company's e-waste policy or returned to the provider.
Conclusion
Mastering the full lifecycle of a security seal—from storage to disposal—transforms a simple component into a cornerstone of your security and compliance strategy.
How ProtegoSeal Can Strengthen Your Seal Program
If this guide reveals gaps in your security protocols, we can help. ProtegoSeal offers not just compliant seals but the expertise to build a robust program around them. To strengthen your supply chain security, contact us for a professional consultation.