A barcode that cannot be immediately recognized by a scanner is a defective product, even if the seal itself is physically intact.
Security seal barcodes are not merely graphical representations of numbers; they are the unique interface connecting your physical security hardware to your digital logistics system. In modern supply chains, a valid barcode transforms a passive lock into an active data point, ensuring your Chain of Custody is digitized, automated, and error-free.
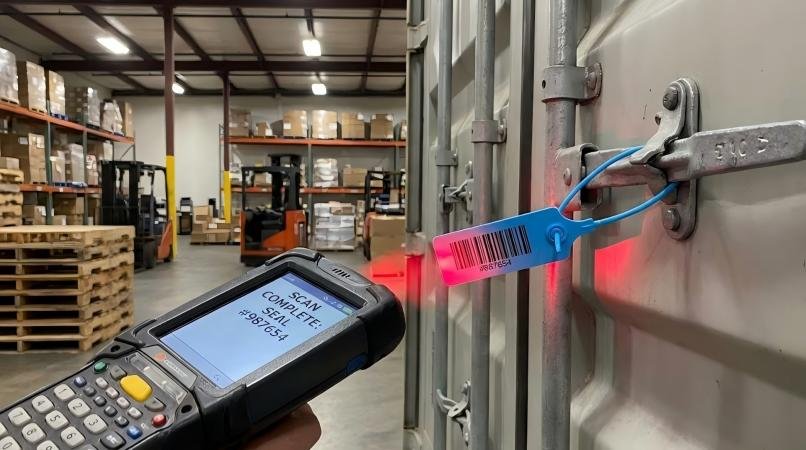

I need to emphasize a critical reality: In the automated logistics of 2026, readability is reliability. As a manufacturer, I often see clients focusing solely on the tensile strength of a seal while ignoring the print quality. However, if a seal requires manual data entry because the barcode is faint or scratched, human error rates skyrocket to over 10%. A high-quality security seal barcode acts as the immutable bridge between the physical reality of the container and the digital reality of your ERP system.
The Anatomy of Security Seal Barcodes: Definition, Features, and Applications
What actually makes a barcode readable by a machine on a curved seal surface? It is not just black bars; it is a precise engineering of contrast and silence.
The anatomy of a functional plastic security seal barcode consists of the "Quiet Zone" (empty margins), the "Start/Stop Characters," and the high-contrast data bars. If any of these elements are compromised by poor manufacturing, the seal becomes a bottleneck rather than a solution.
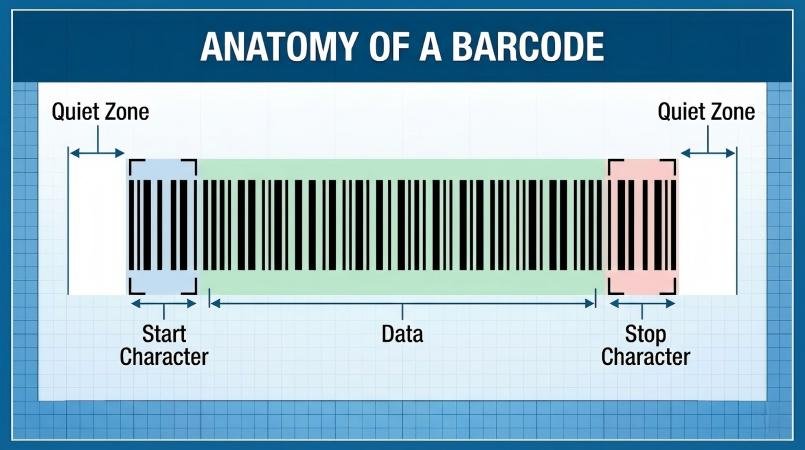
Decoding the Structure
To understand why cheap seals fail scan tests, we must look at the surface obstacles. Security seals often have small, irregular, or curved printing areas.
- The Quiet Zone: This is the blank white space on both ends of the code. I frequently see manufacturers trying to cram a long number onto a small tag, cutting off this zone. Without this "silence," the scanner cannot detect where the code begins.
- Contrast Ratio: The scanner reads the reflectivity difference (light). If the plastic seal material is too dark (like dark blue or black) and the laser marking isn't deep enough, the contrast fails. This is why white or yellow seals are industry standards for barcode applications.
- Symbology: This is the language of the code. GS1-128 (Code 128) is preferred for seals because it is compact and handles alphanumeric data well, whereas older formats like Code 39 take up too much physical space on a small seal flag.
How Does Unique Identification Enhance the Chain of Custody?
Why is non-repeatable serialization the absolute backbone of supply chain security? Because duplicate numbers destroy the legal validity of your shipment.
Unique identification (UID) ensures that every single asset has a distinct digital fingerprint. When a high-security bolt seal is scanned at the origin and again at the destination, it mathematically proves that the asset has moved through the authorized path without substitution.
![]()
The Power of "One-Time Use" Data
In my experience resolving lost cargo disputes, the most dangerous issue is "Duplicate Numbers."
Imagine a sophisticated thief buys the same model of seal you use. They break your seal, steal the goods, and apply their own seal. If you rely on human eyes to check the number, they might get away with it.
However, with GTIN unique identification encoded in a barcode, the system is rigid. When your warehouse scans the fake seal, the database—which expects a specific serial sequence linked to that order—will flag an "ID Mismatch" or "Duplicate Entry" error. The barcode prevents the "human eye" trick, creating a digital tripwire that manual checks simply cannot provide.
1D vs. 2D: Which Barcode Format Fits Your Specific Security Seal Type?
Should you stick with the classic lines (1D) or upgrade to the square blocks (2D/QR)? The choice isn't about style; it's about hardware compatibility and data density.
1D Barcodes are the industry workhorse for simple ID numbers compatible with all laser scanners, while 2D Barcodes (like QR codes) offer massive data capacity and error correction but require camera-based scanners (imagers).
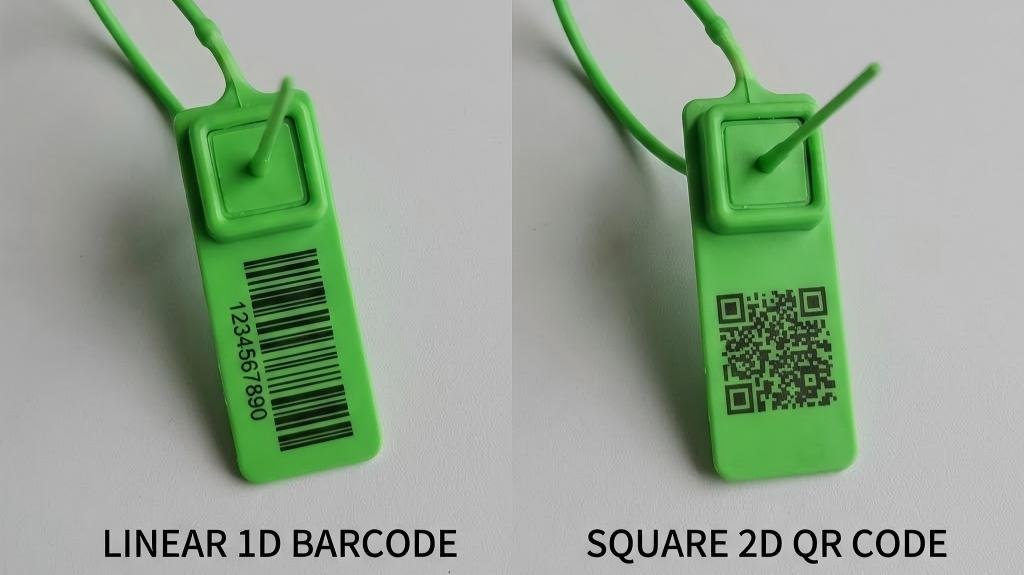
Choosing the Right Format for Efficiency
I often advise clients to audit their scanning hardware before choosing a seal.
- 1D Barcodes (Linear - Code 128):
- Best for: Bolt seals, Cable seals with limited space.
- Pros: Readable by standard laser guns found in every warehouse. High scan speed.
- Cons: Limited data (10-15 chars max). If a bar is scratched vertically, the code dies.
- 2D Barcodes (QR / Data Matrix):
- Best for: Large flag plastic seals, tote seals.
- Pros: Data Matrix codes can lose 30% of their surface to damage and still scan due to error correction algorithms. They can store URLs for customer verification.
- Cons: Standard legacy laser scanners cannot read them. You must upgrade to 2D Imagers or use smartphones.
| Feature | 1D Barcode (Linear) | 2D Barcode (QR/Data Matrix) |
|---|---|---|
| Scanner Type | Laser or Imager | Imager or Camera Only |
| Data Capacity | Low (Serial Number only) | High (URL, Batch, Date) |
| Damage Tolerance | Low (Zero redundancy) | High (Error correction) |
| Space Required | Wide horizontal space | Small square space |
Why Is Laser Engraving Critical for Barcoded Security Seals?
Why do ink-printed barcodes fade into useless smudges while laser markings survive years of abuse? The secret lies in the molecular change of the material.
Laser engraving is critical because it captures the data inside the plastic, not just on it. Unlike hot stamping or thermal transfer which applies Ink, laser marking burns carbon into the seal's structure, creating a permanent, unalterable mark.
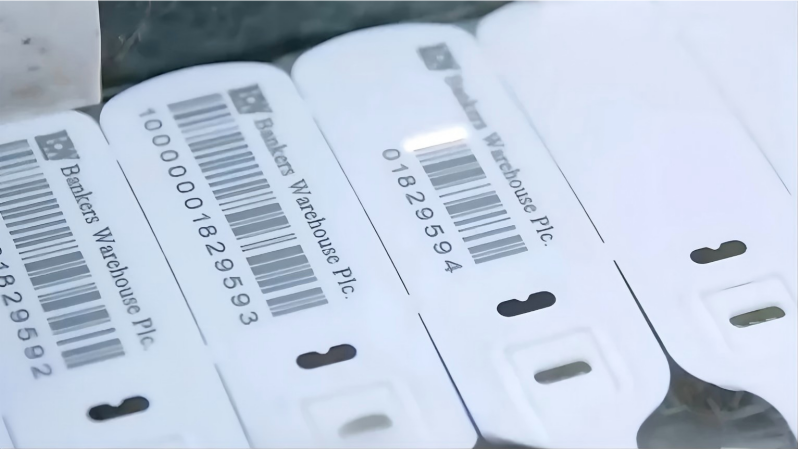

The Permanence of Carbonization
In our factory, we add specific laser-sensitive additives to the raw material. When the laser beam hits the plastic, it causes a chemical reaction called carbonization.
This offers three non-negotiable benefits:
- Tamper Evidence: You cannot "erase" a laser barcode without physically carving out the plastic, which leaves obvious evidence of tampering.
- UV & Chemical Resistance: Ink fades in sunlight and dissolves with solvents. Laser markings are impervious to UV rays and harsh chemicals, ensuring the barcode remains readable even after 45 days at sea.
- Edge Definition: Lasers print at high DPI (dots per inch). This sharpness is essential for the scanner to distinguish between the bars and spaces, guaranteeing a high "First Pass Read Rate."
Preventing Data Duplication During the Manufacturing Process
How can you trust that the seal you receive today doesn't duplicate a number from a shipment sent six months ago? Rigorous manufacturing IT controls are the answer.
Preventing data duplication requires a "Closed Loop" production system where the laser marking machines are synchronized with a central Cloud Inventory Management server to retire numbers immediately upon use.

The "Zero-Duplicate" Protocol
I have witnessed the operational disaster caused by duplicate seals—two containers with the same ID effectively turn into "ghost cargo."
To prevent this, we implement a strict protocol:
- Server Allocation: The laser machine does not generate numbers. It requests a block of numbers from the central server.
- Vision Inspection: This is the fail-safe. Immediately after the laser marks the seal, a high-speed camera scans the barcode. This system checks quality (is it readable?) and history (has this string appeared before?).
- Auto-Reject: If the camera detects a duplicate or a low-contrast code, an air jet kicks the bad seal into a locked reject bin. We do not rely on human inspection; we rely on automated validation to guarantee that every single barcode you receive is a unique digital identity.
Conclusion
A security seal barcode is the critical link between your physical cargo and your digital records. By understanding the anatomy of a scan, choosing the correct 1D or 2D format, and insisting on laser-engraved uniqueness, you eliminate data gaps and secure your supply chain.
Digitize Your Security with ProtegoSeal
Don't let unreadable barcodes break your chain of custody. At ProtegoSeal, we specialize in high-contrast, laser-engraved security seals that guarantee 100% scan rates. Whether you need serialized Code 128 or complex QR code solutions, our automated vision inspection systems ensure every seal is unique and perfect. Contact us today to request scan-tested samples.